
While we all know about logistics and worldwide supply chain management, reverse logistics (at least the term) remains elusive to most. Simply put, reverse logistics is about taking the product from customers and bringing it back to the manufacturers through the supply chain network.
Mostly, reverse logistics is relevant for eCommerce companies with easy return policies, like Amazon. According to the Reverse Logistics Association, return rates for e-commerce purchases are three to four times higher than those for in-store purchases. In fact, Amazon leads the reverse logistics industry with around 13% market share.
Here is everything you need to know about the reverse logistics industry to make it easier for you to get into this industry.
What is Reverse Logistics?
Effective reverse logistics is that part of the supply chain management that transports the goods and products from the customers to the manufacturers. Some of the reverse logistics examples are return, reuse, refurbish, repair, and recycling. Usually, reverse logistics comes into play after the customer receives the products and starts the recycling or return process.
As you can see, reverse logistics flow follows the opposite path of your traditional supply chain. This is more prevalent where the manufacturer or the seller is also responsible for refurbishing or recycling the product. However, effective reverse logistics or returns management is also increasing in popularity due rise in no-fuss return policies of new-age eCommerce brands.
How does reverse logistics work?
The process for reverse logistics or returns management is the same as your traditional logistics. The reverse logistics work requires planning shipments, managing shipping loads, and cleaning the containers. The customer pings for the return of the product. The customer receives the guidelines to prepare the product for transport. Then, the delivery driver picks up the product and delivers it to your intended hub thus completing the reverse supply chain.
Now, reverse logistics is not only reserved for customer returns and refurbishing of products. This process also returns unsold goods with wholesalers to the parent company. The same happens with goods intended for remanufacturing or repair departments.
For example, packaged food companies like the beverage industry use reverse logistics to recollect expired products from the sellers. In the case of equipment rentals or leasing, you ping the customer instead of the other way around. The rest of the steps are the same for this one.
Types of Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics is an umbrella term that covers a variety of reverse logistics processes. Here are the different types of reverse logistics.
- Receiving returns: This involves returning the products after the customer has purchased it. For brick-and-mortar purchases, the return happens at the store where the product was first bought. And, for retailers, it is returned using the same delivery channel.
- Resale of returns: If the returned product is fully functional, it is repackaged and prepared for resale to other customers. The original customer is compensated with a refund.
- Processing returns: The item is thoroughly checked and logged into the system during the return procedure. This scrutiny prepares the items for storage, repair, or resale.
- Salvaging returns: If the product is beyond repair, individual parts are taken out to be re-used as spares or resold as used products.
- Refurbishing returns: If the product can be repaired, it will undergo corrective procedures and be prepared for resale.
- Donating returns: Some suppliers donate outdated returned products to claim tax relief based on the CSR provisions.
- Recall returns: Occasionally, when businesses notice mass defects in their products, the companies initiate a recall to recollect every single product to correct the issue.
- Return cycling: Broken products have little-to-no value, but their parts might have. Under return cycling, the returned products are broken down and safely recycled.
Reverse vs. Traditional Logistics
The fundamental difference between reverse and forward logistics is the direction in which products move along the supply chain. However, let’s check a brief comparison between the two major types of logistics will help you better understand them.
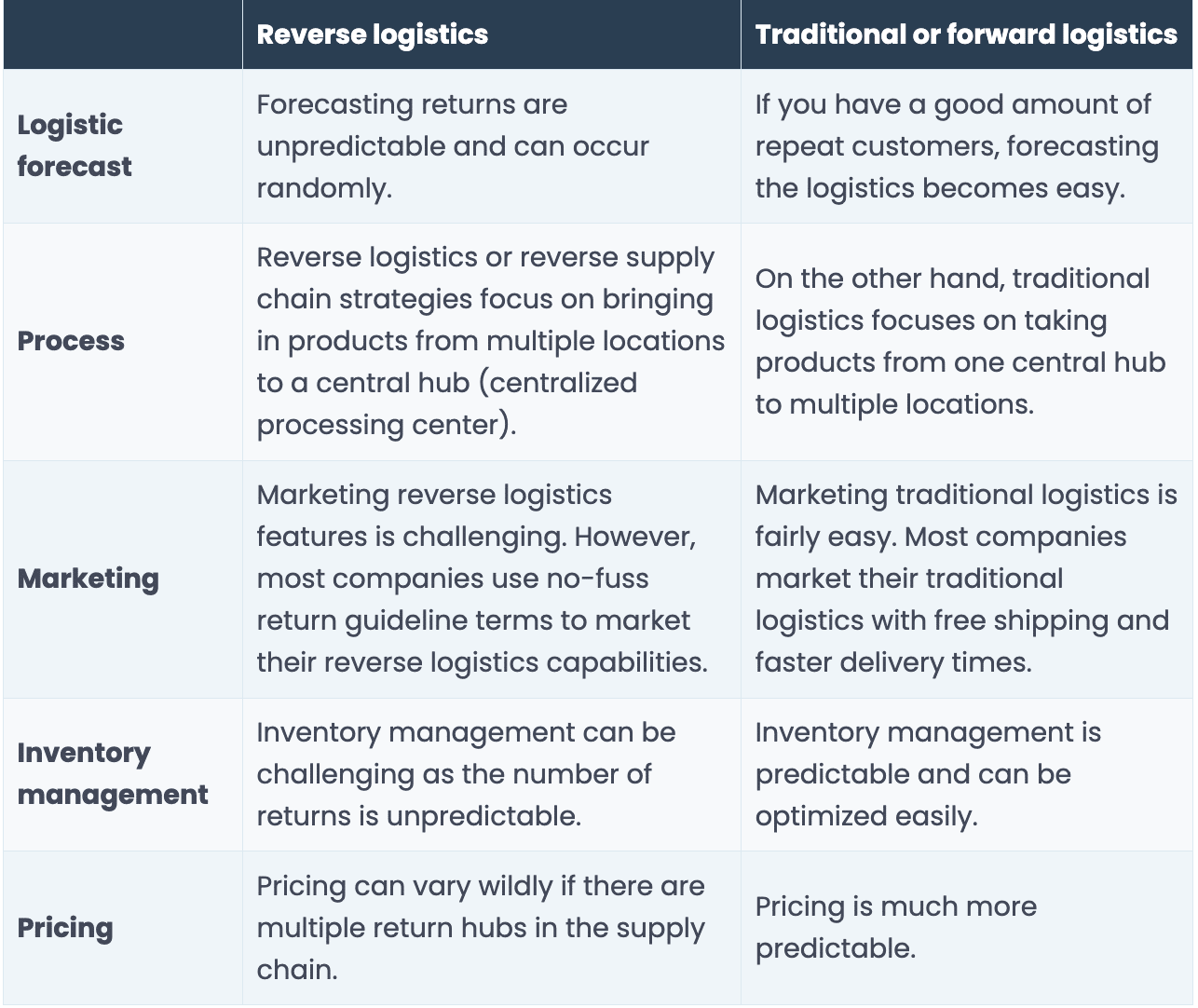
Why is it so Important for Your Business?
Reverse logistics can lead to increased returns, driving up supply chain costs and impacting business profits. Therefore, here are a few reasons why reverse logistics management is important for your business.
- Creates efficient flow of goods
Reverse logistics create an efficient flow of goods for your company. Following the best practices will decrease environmental risks, reduce overall costs, and increase the ROI of your processes. Lastly, it helps complete the product life cycle by boosting the efficiency of the traditional supply chain. - Maintains a circular economy.
The main focus of the circular economy is controlling climate change, reducing waste, mitigating pollution, and encouraging biodiversity. Investing in the circular supply chain management for your company also presents your organization as an environmentally conscious entity. The circular economy starts with traditional logistics and ends with reverse logistics. - Helps adhere to sustainable policies of different Governments
Reverse logistics and the resulting circular economy help your organization to conform to the various sustainable demands of different government bodies.This could include recycling waste or proper disposal of hazardous waste throughout the supply chain. Most governments and countries are developing guidelines for landfills and recycling. Disregarding these outlines will result in hefty penalties and fines.






